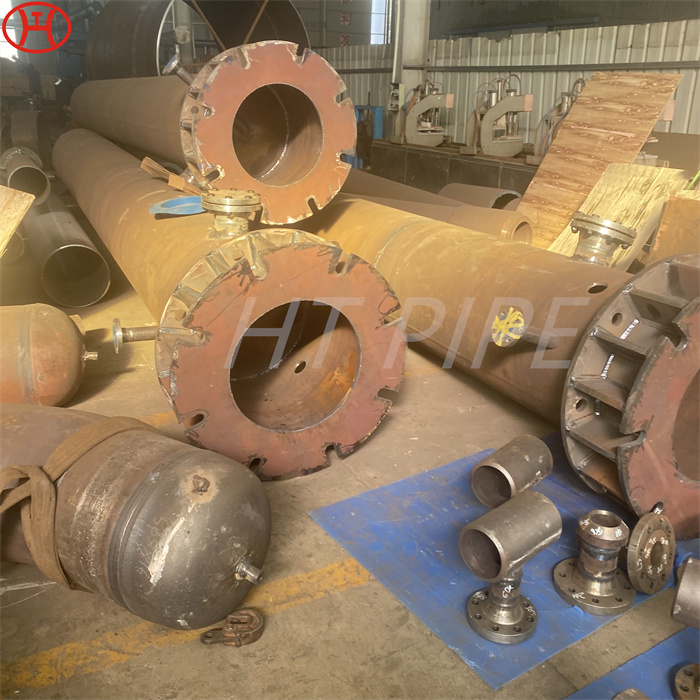
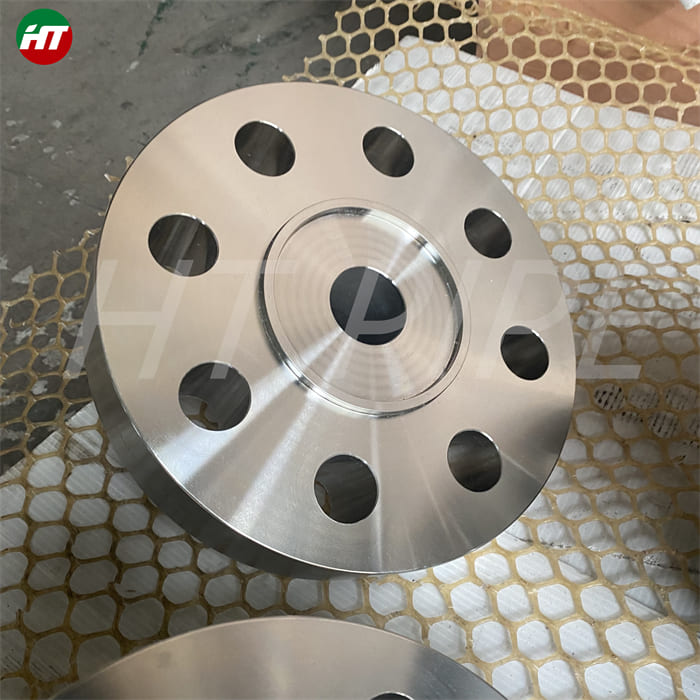
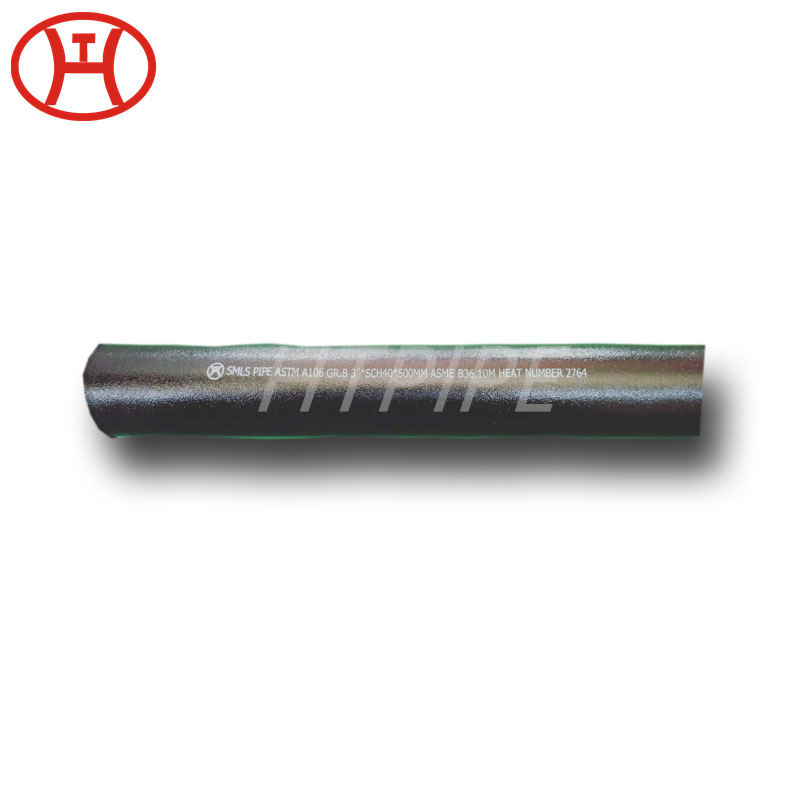
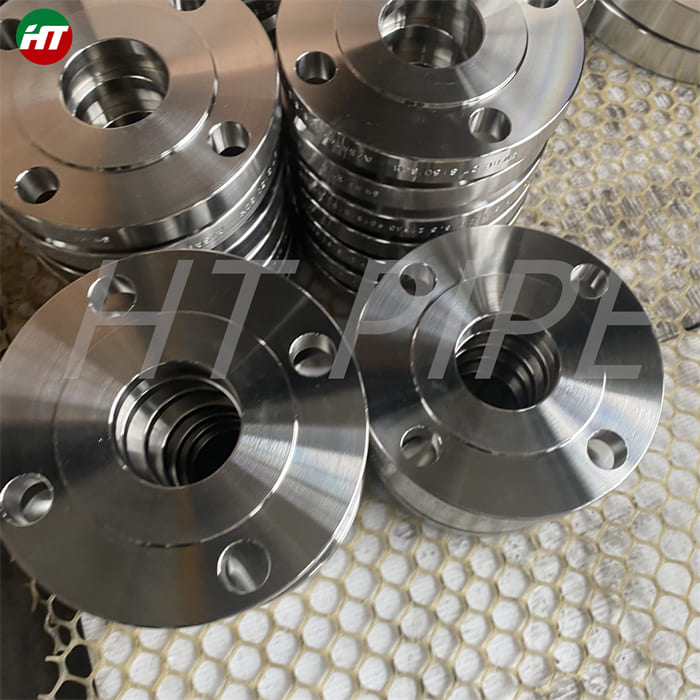
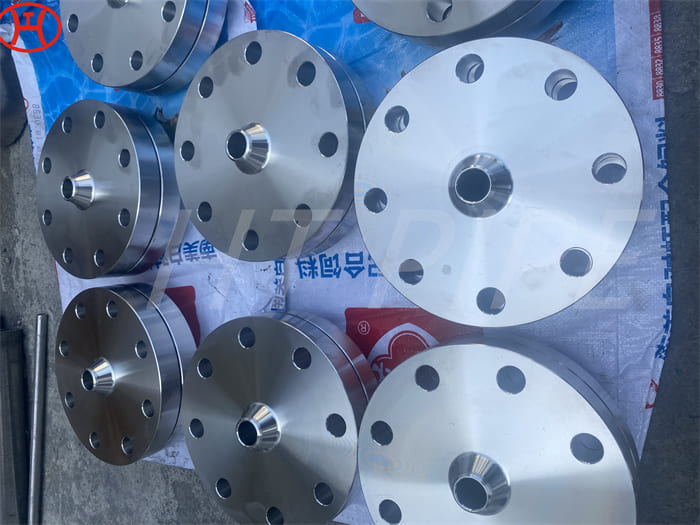
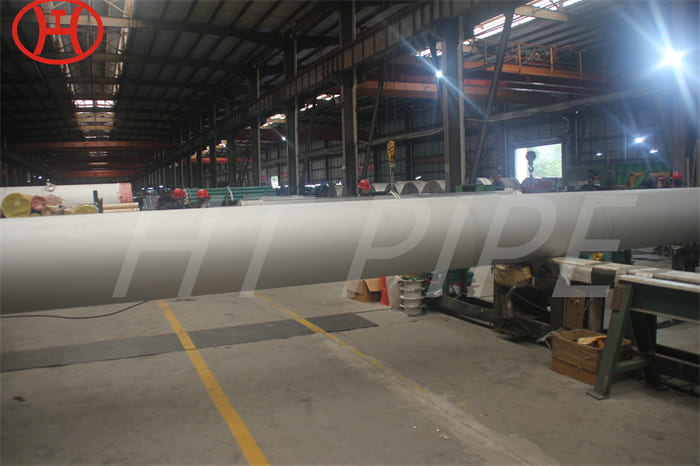
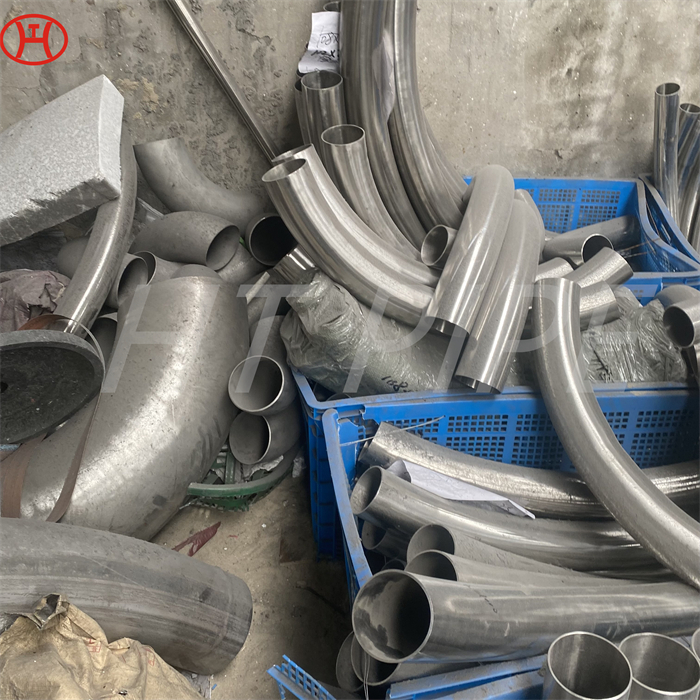
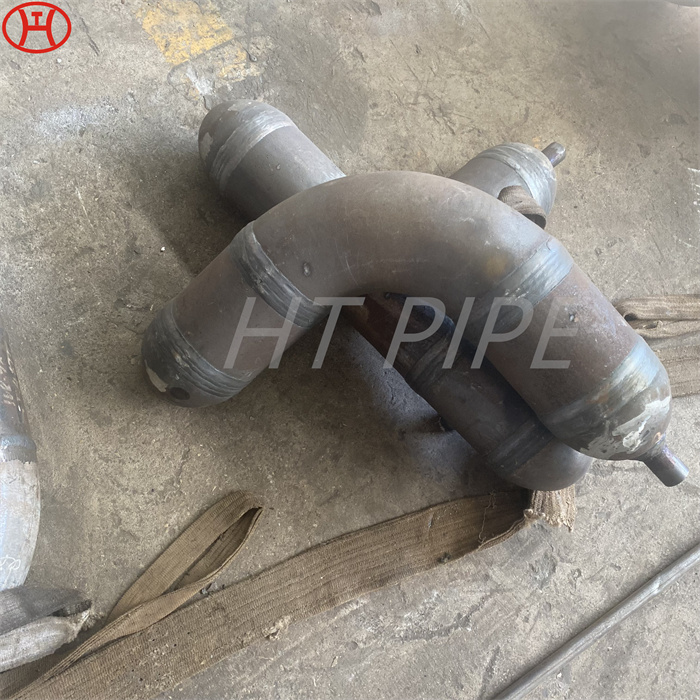
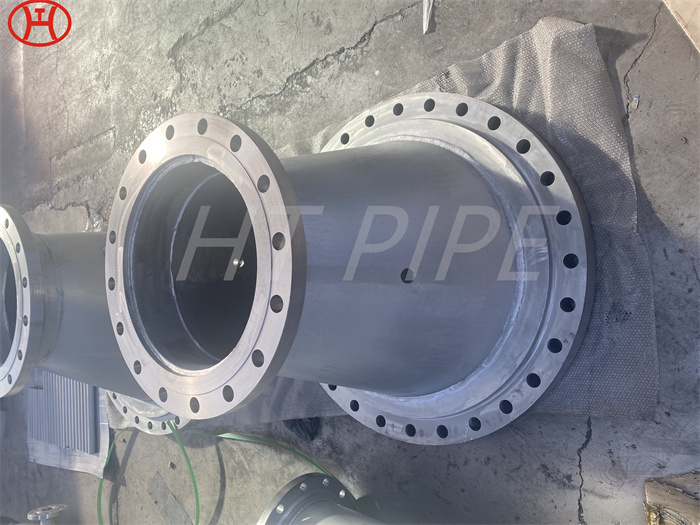
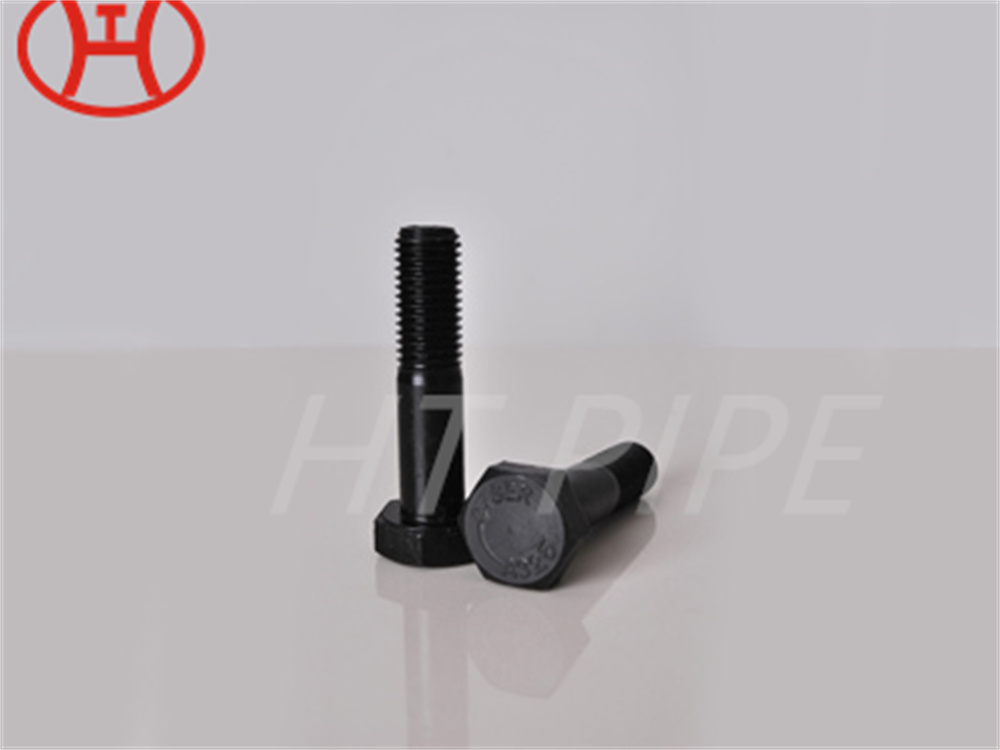
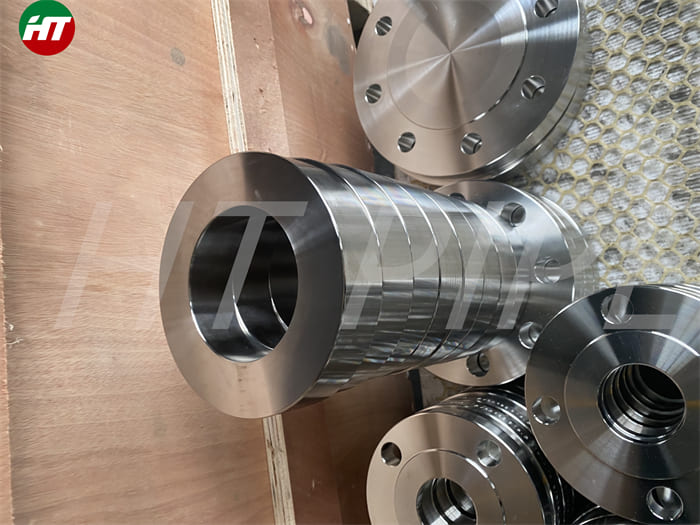
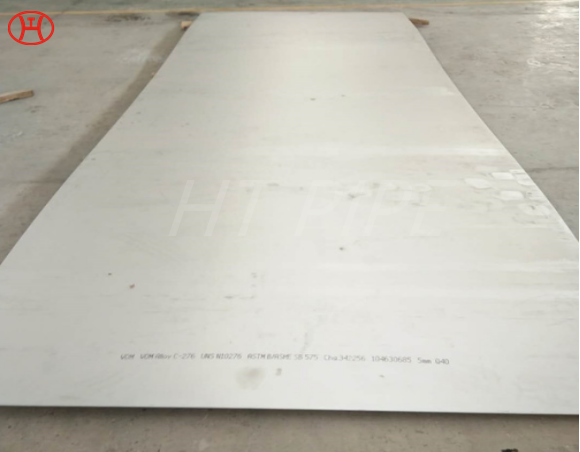
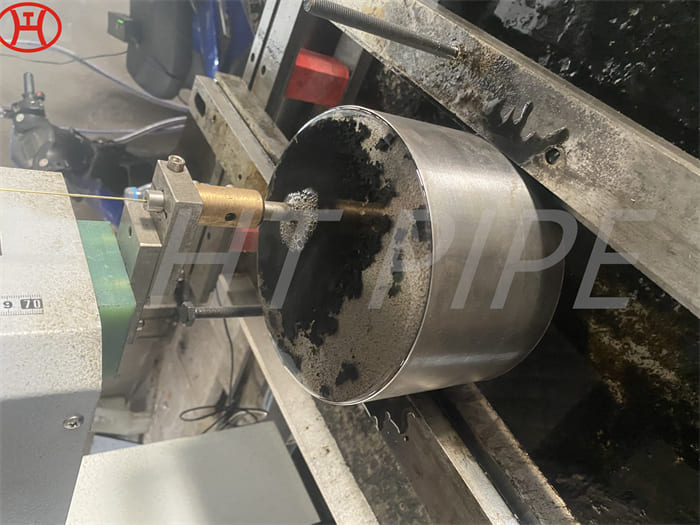
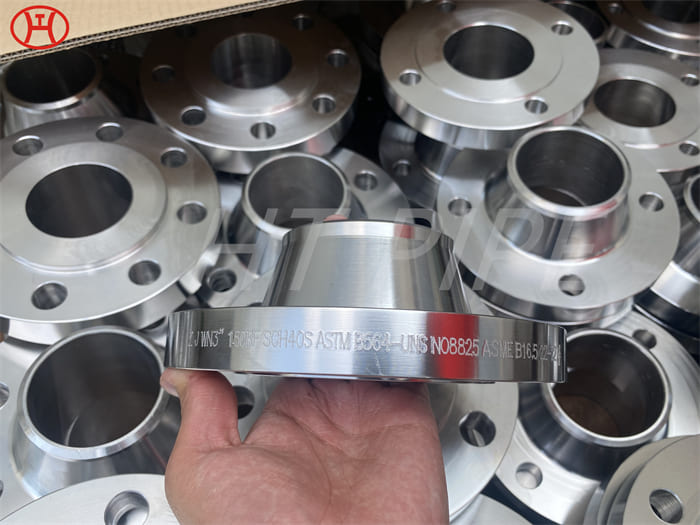
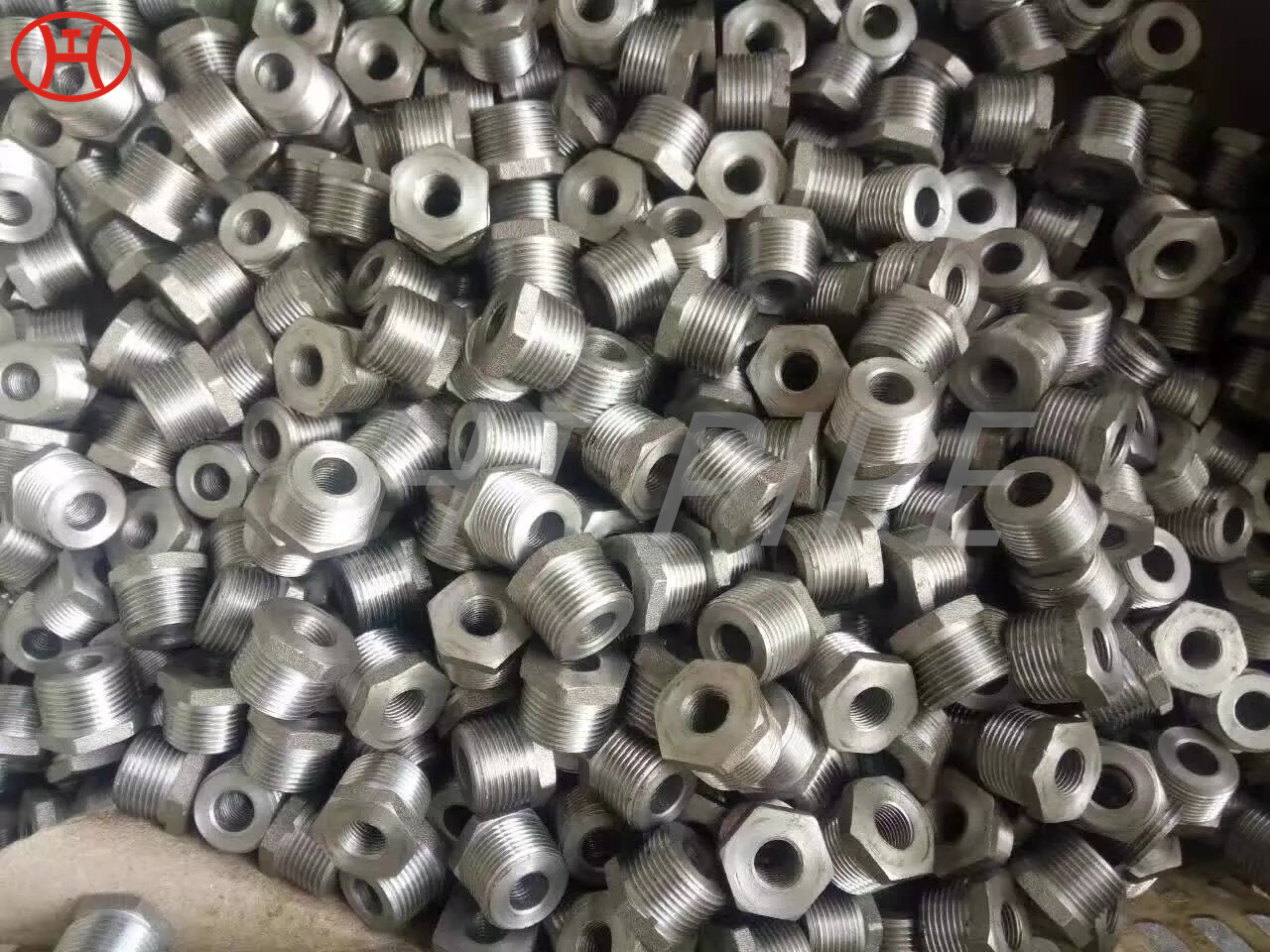
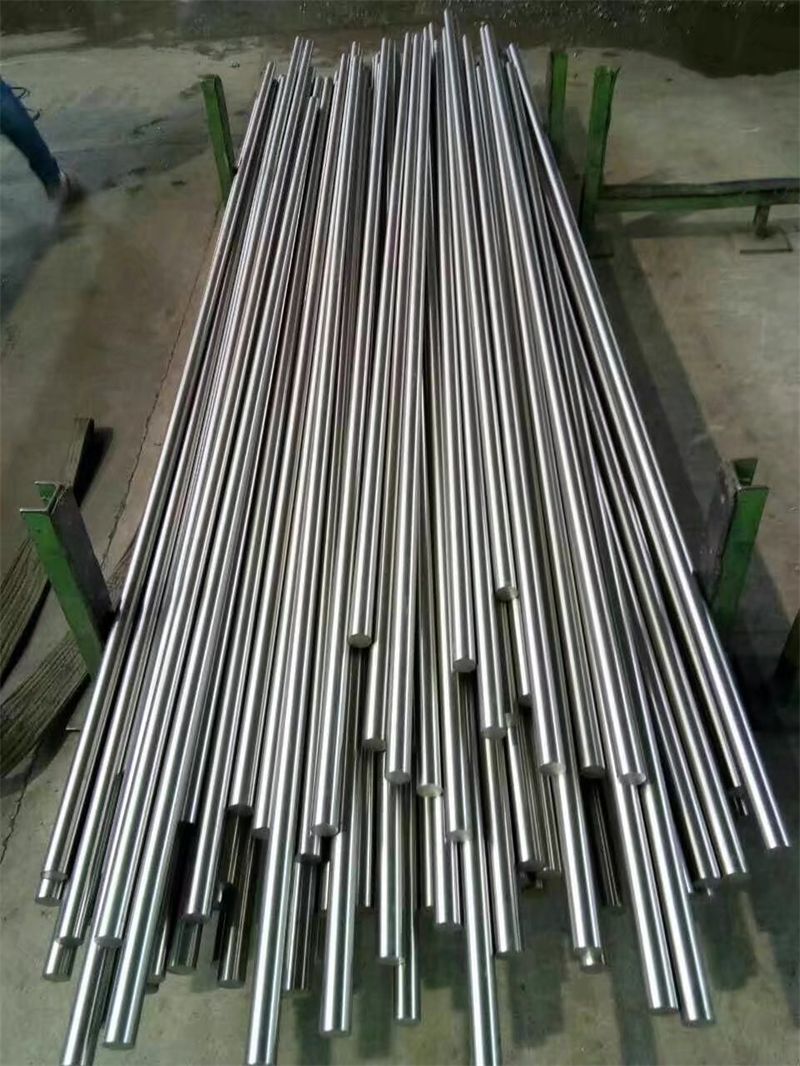
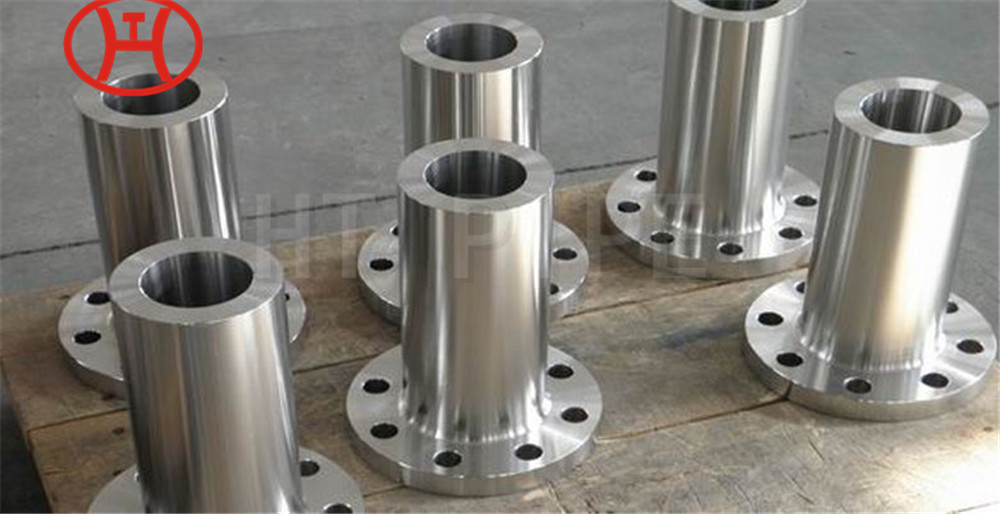
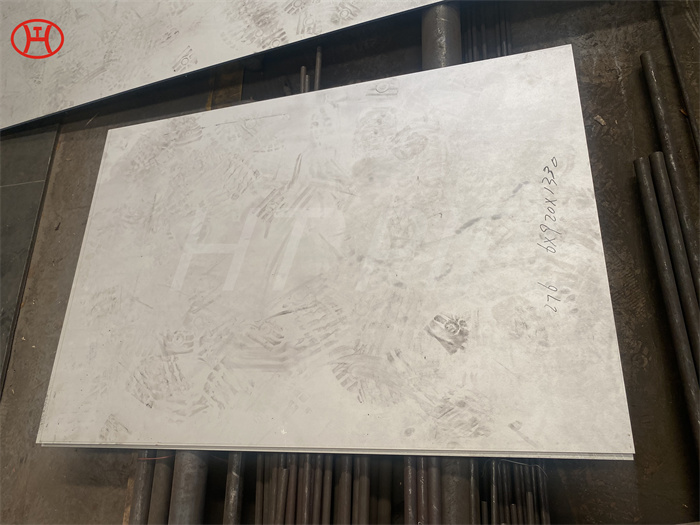
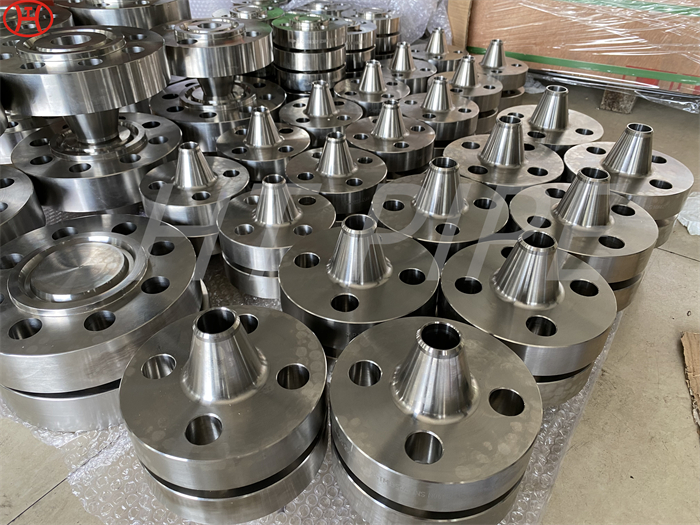
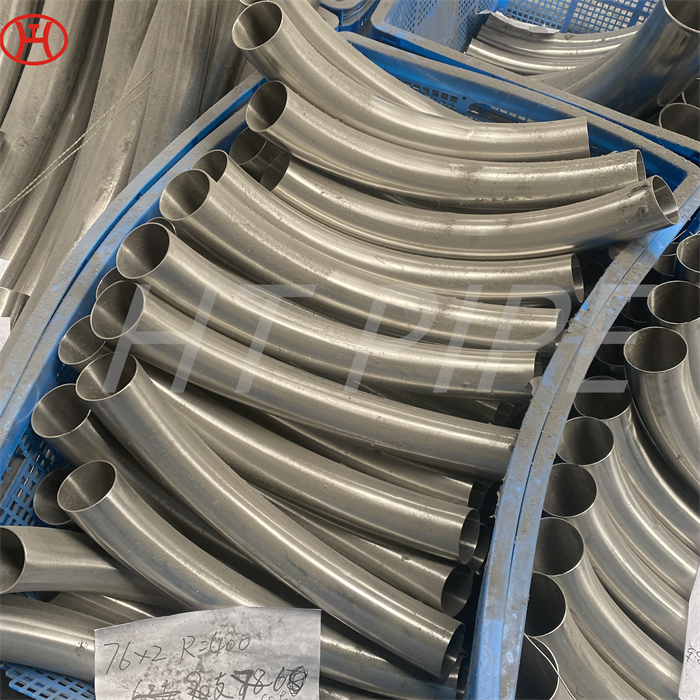
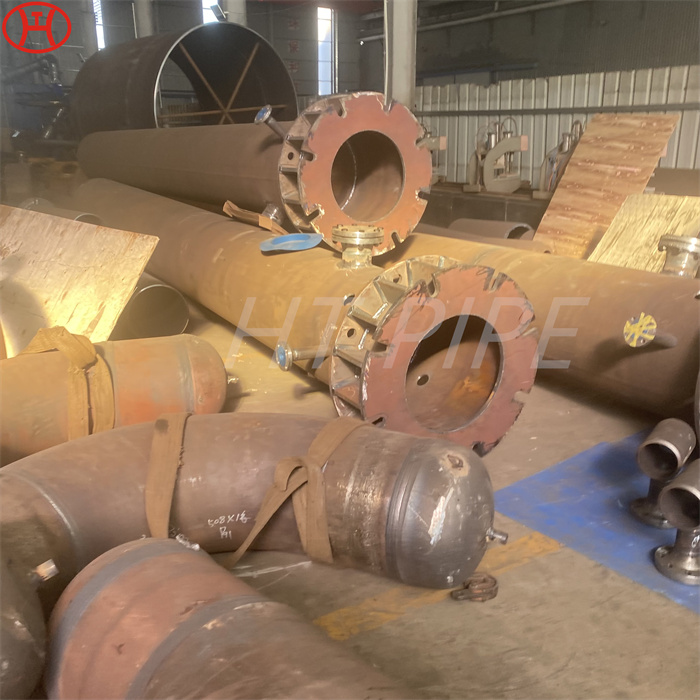
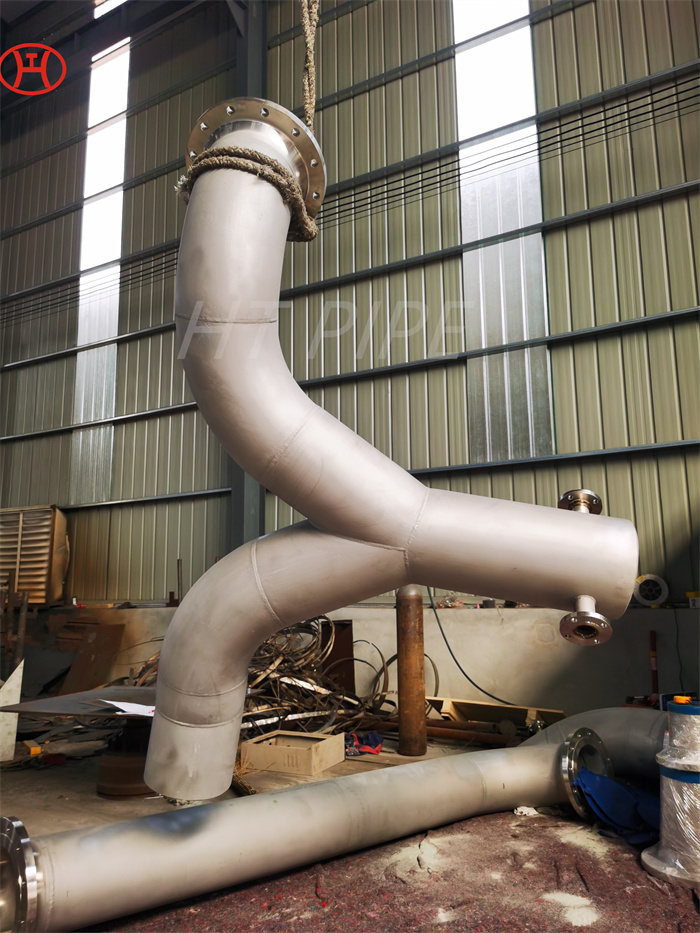
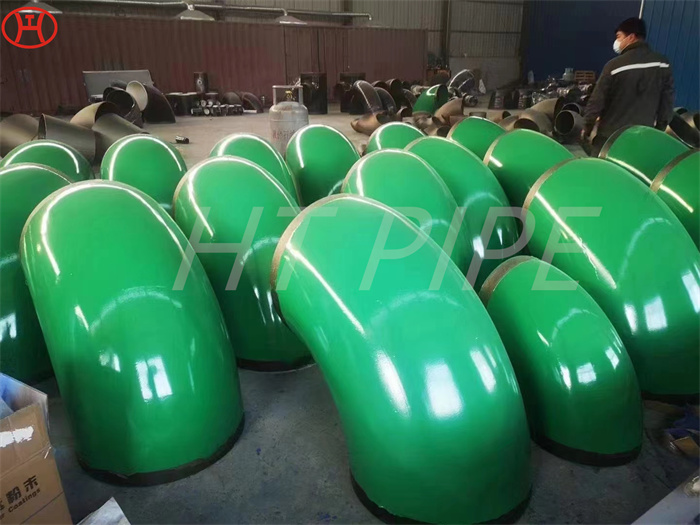
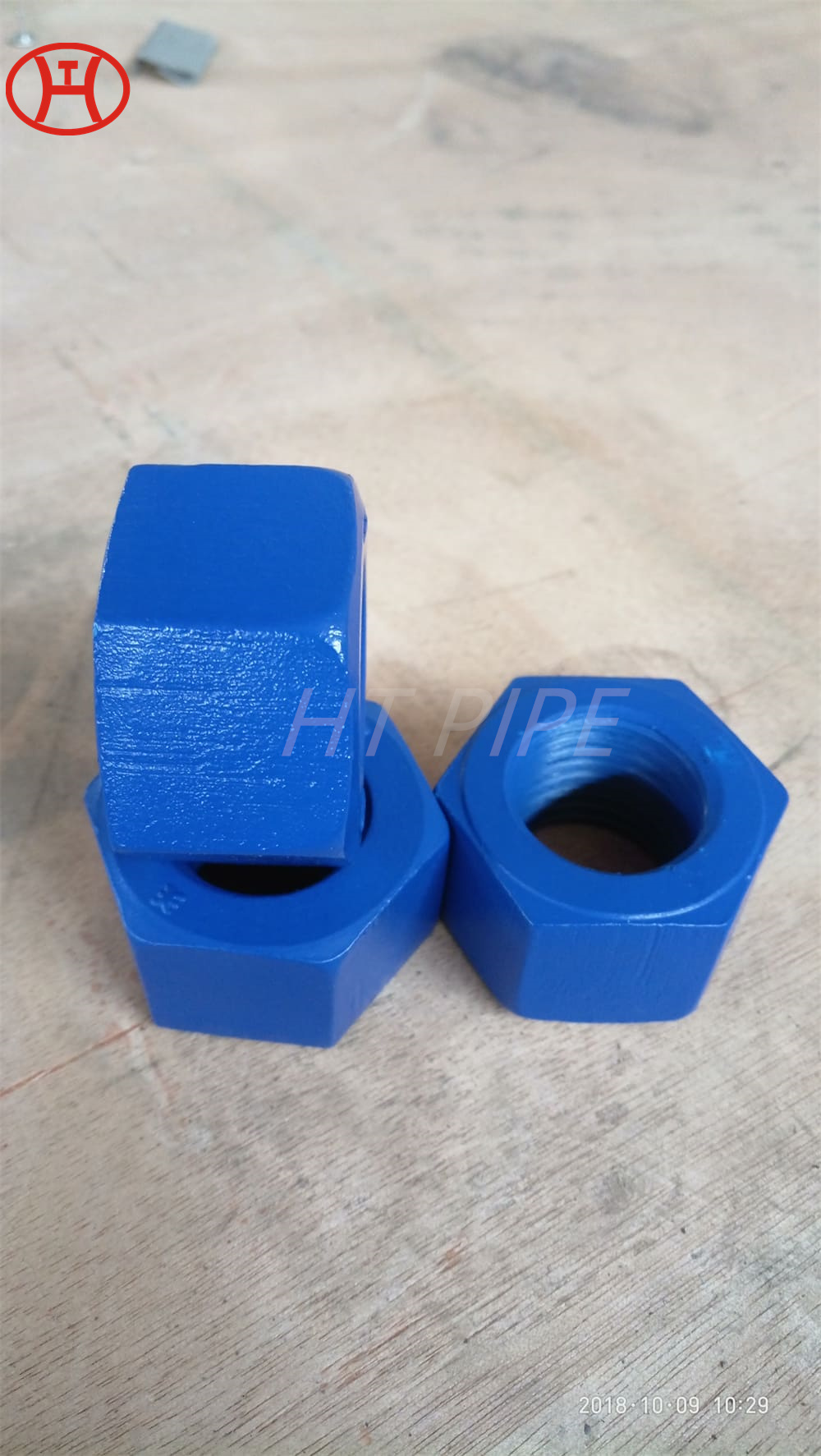
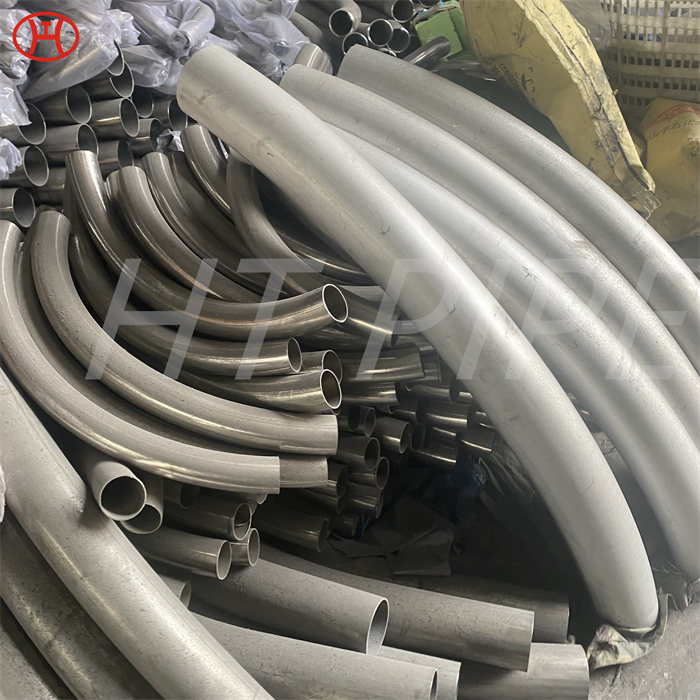
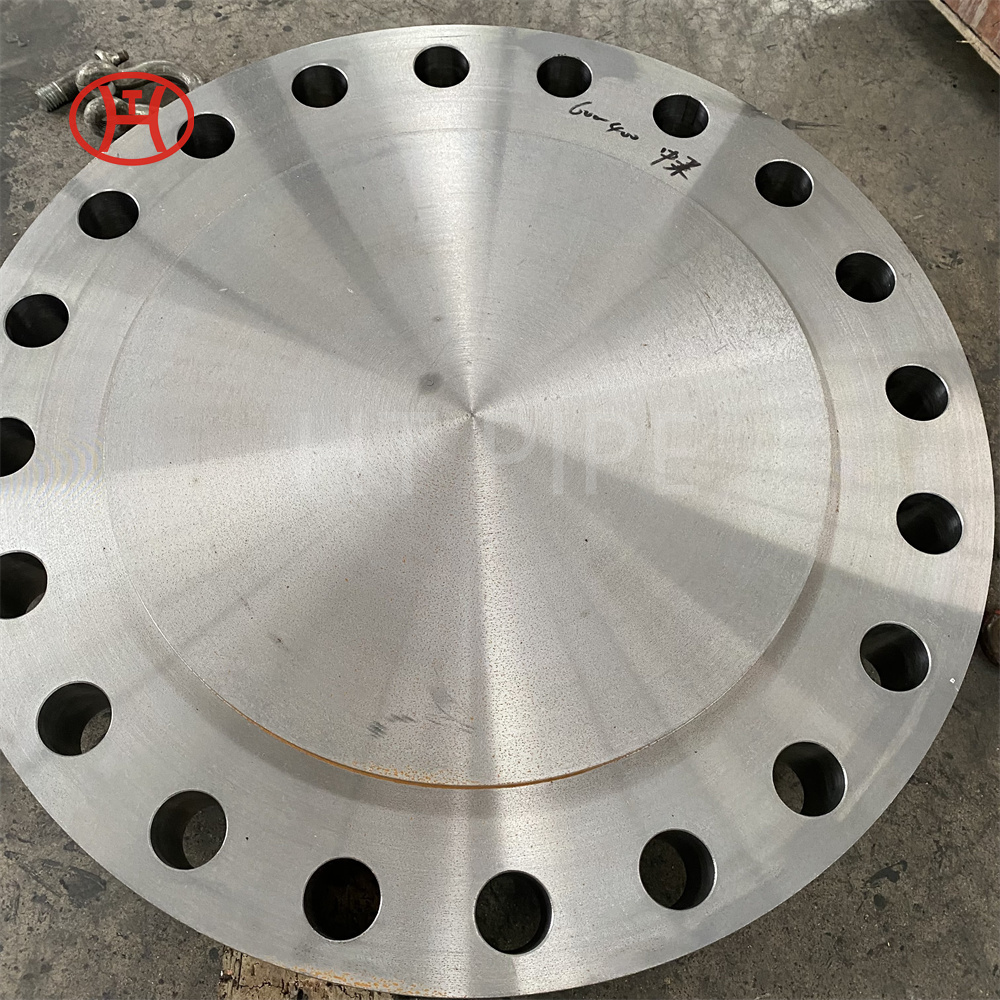
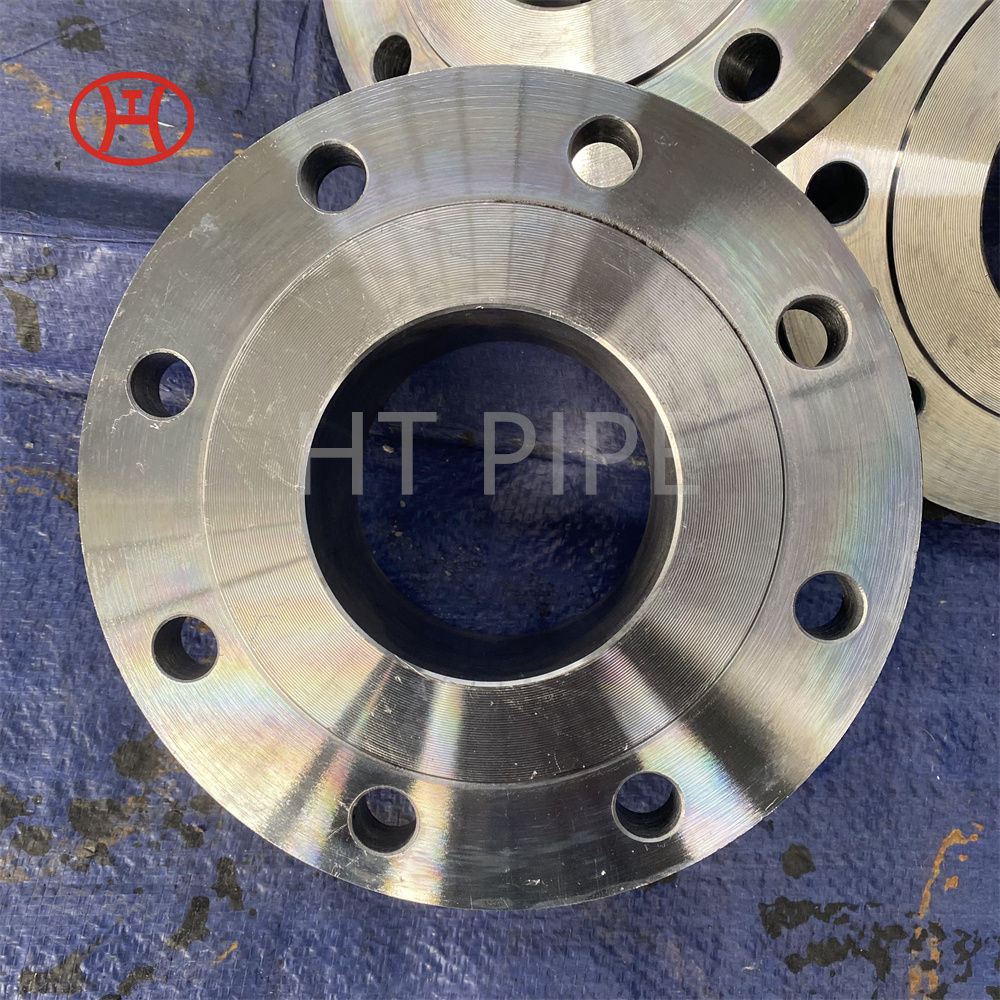
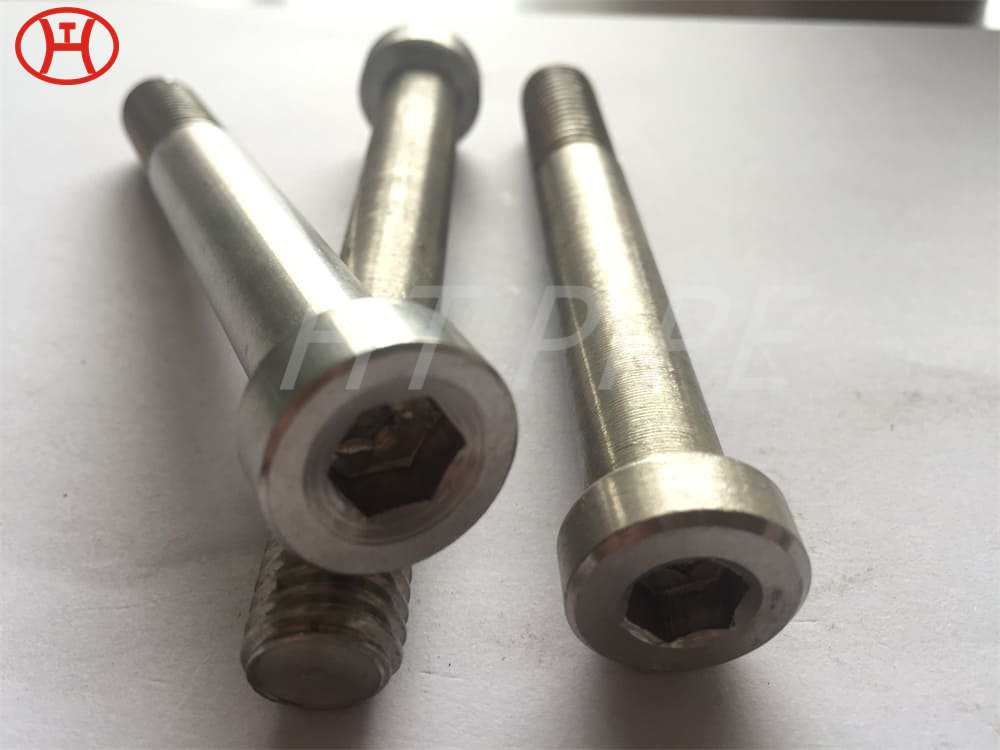
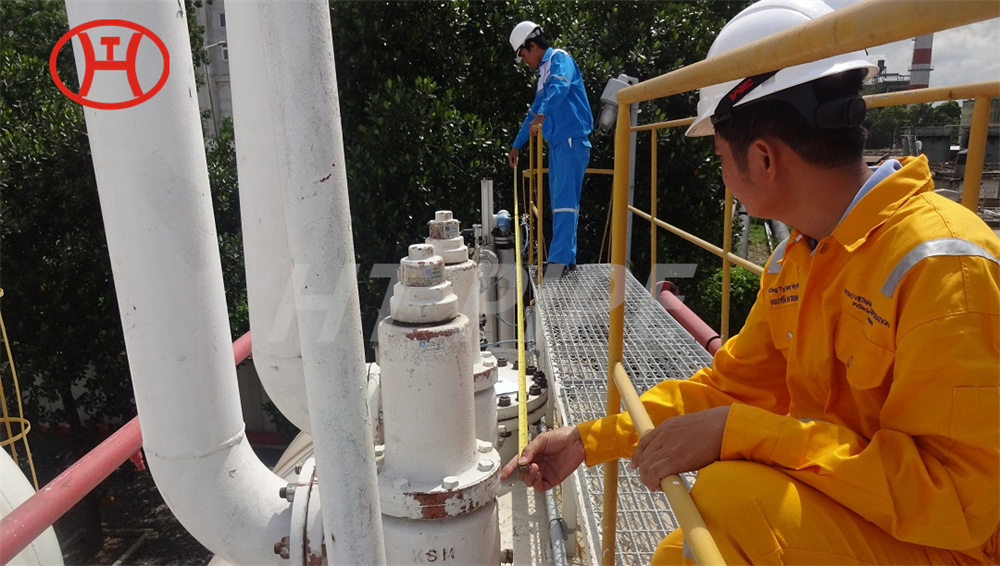
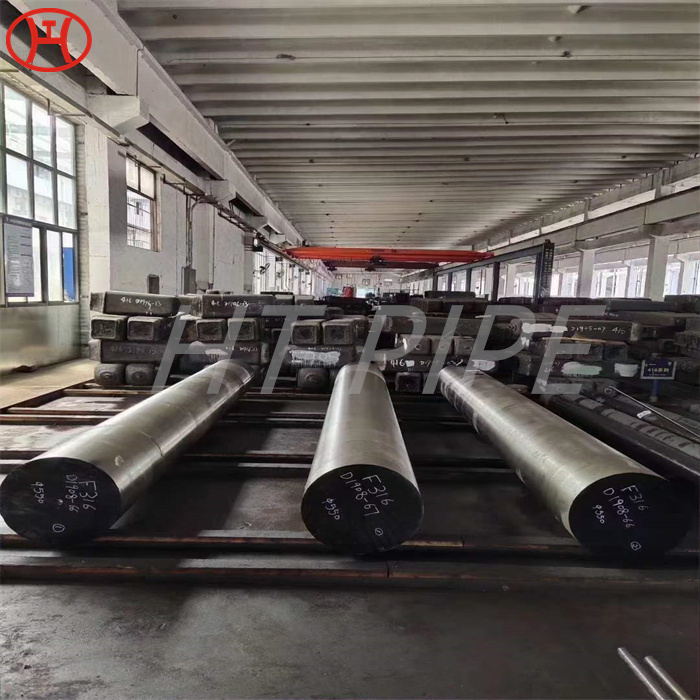
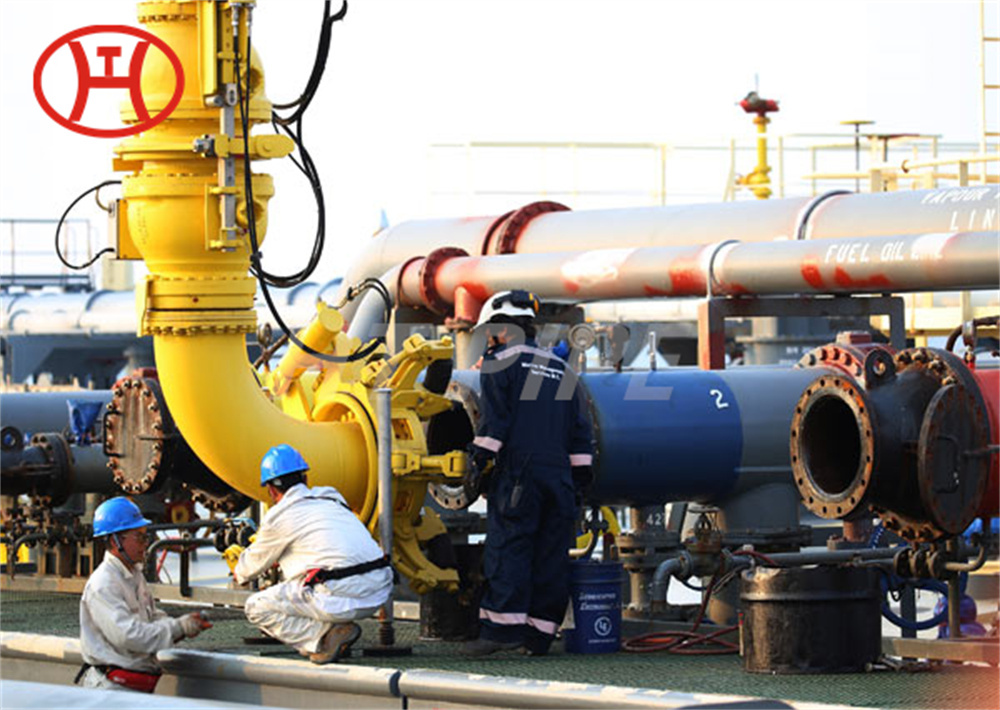
hastelloy c276 2.4819 piping with pipe fittings flanges
Hastelloy C-276 resists the formation of grain boundary deposits in the weld heat affected zone, making it a candidate material for most chemical and petrochemical processing applications in the as-welded state. The alloy resists general and localized corrosion, including pitting, crevice corrosion and stress corrosion cracking.
Hastelloy C276 is used in rotors, bolts, shafts, blades and other components in marine applications and other industries including pollution control; food, waste and chemical processing; paper work; and multipurpose plants. Tungsten has been added to this versatile nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy to resist crevice corrosion, stress corrosion cracking and pitting corrosion. Hastelloy C 276 is resistant to chloride and sulfur mixtures and is ideal for flue gas desulfurization applications.
Hastelloy C-276 alloy is a nickel-molybdenum-chromium wrought alloy, a general purpose corrosion-resistant alloy. Alloy C-276 is an improved forged version of Alloy C because it generally does not require solution heat treatment after welding and greatly improves machinability. The alloy resists the formation of grain boundary precipitates in the weld heat affected zone, thus making it suitable for most chemical process applications in as-welded conditions. However, in environments where C-276 alloy welded joints are eroded. C-22 welding filler material should be considered. Alloy C-276 has excellent resistance to localized corrosion and oxidizing and reducing media. Due to its versatility, C-276 alloy can be used in locations or multi-purpose plants where “uneasy” conditions may occur.