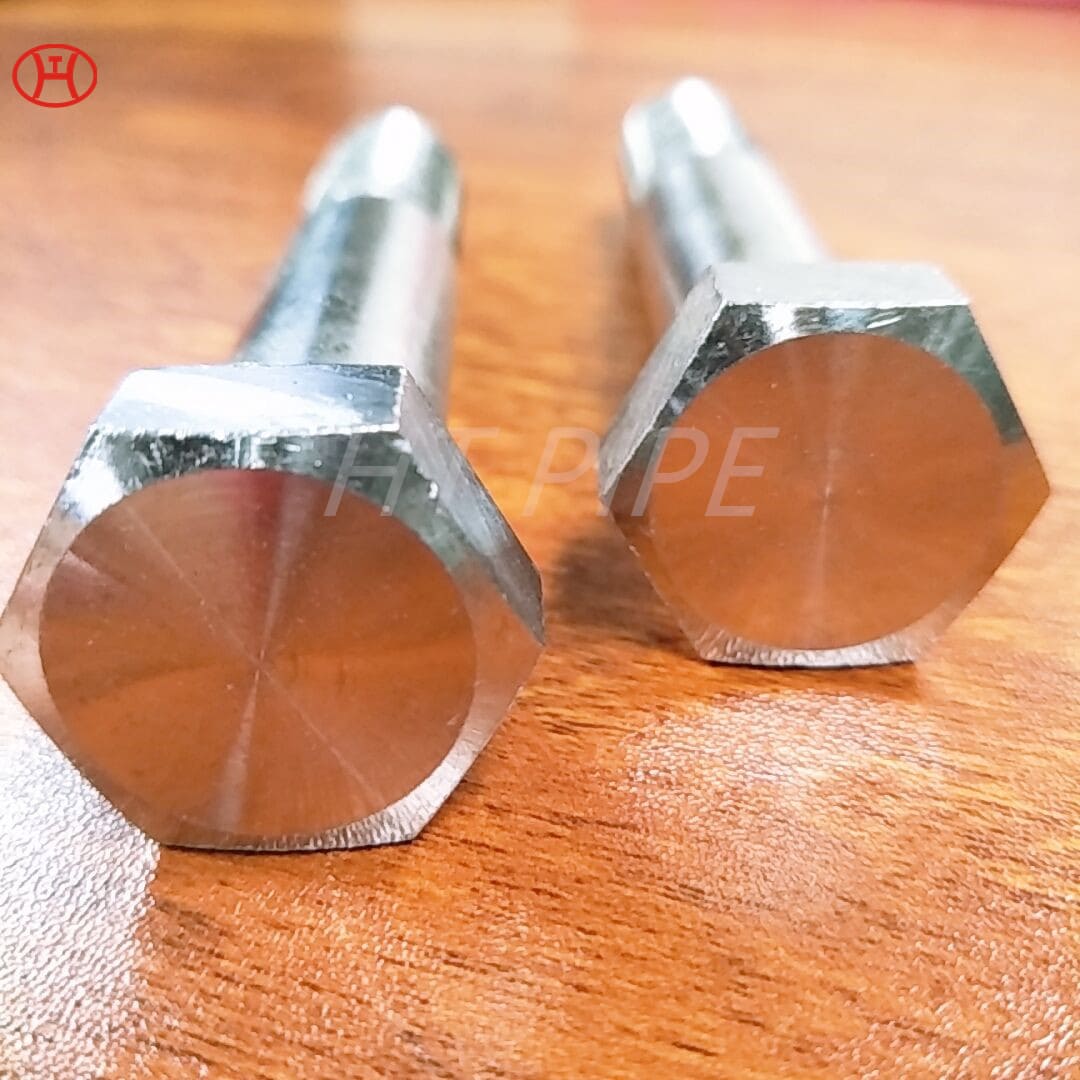
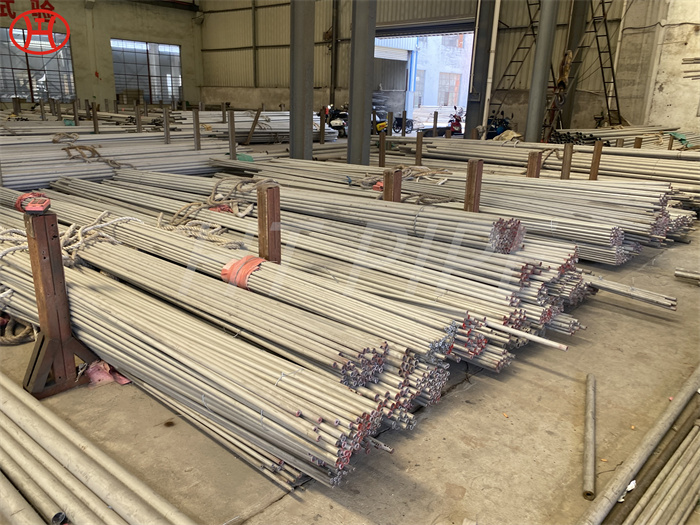
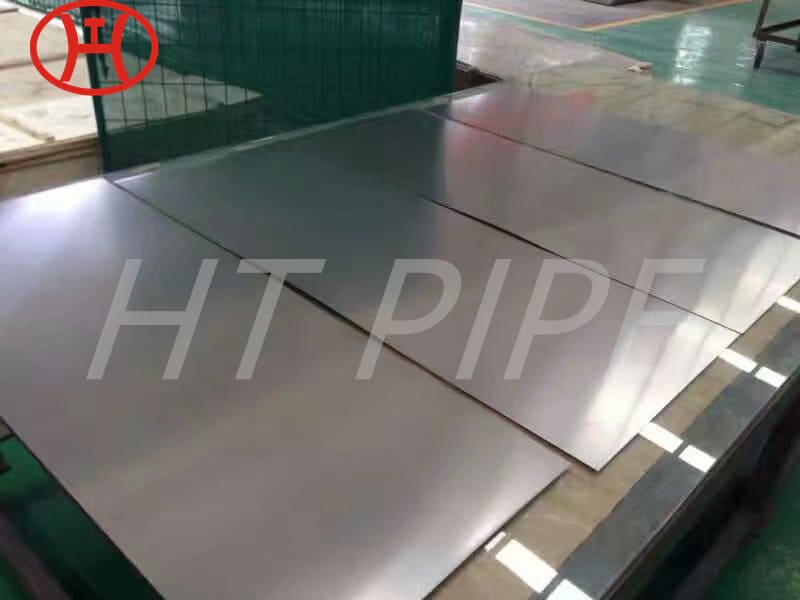
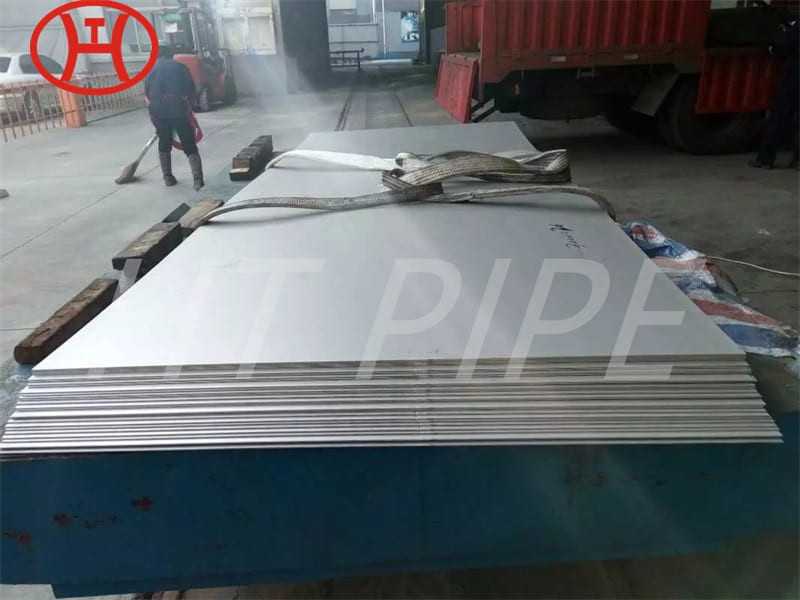
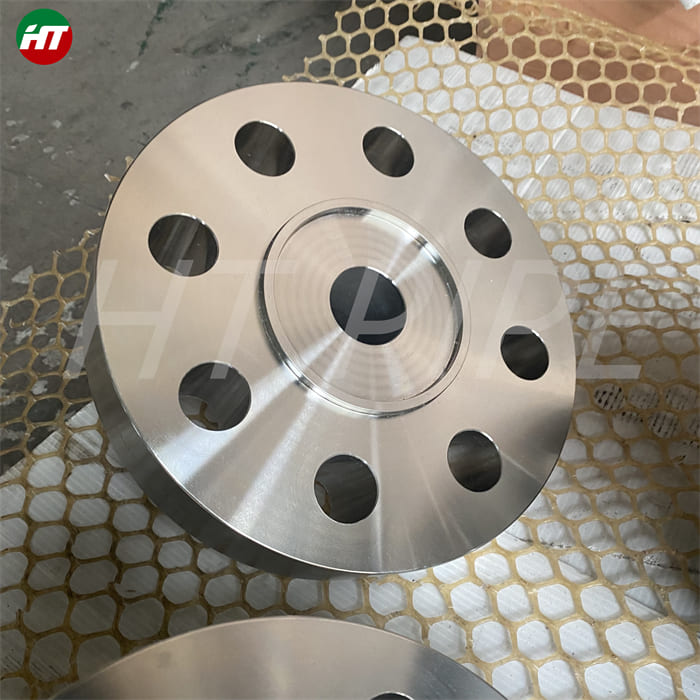
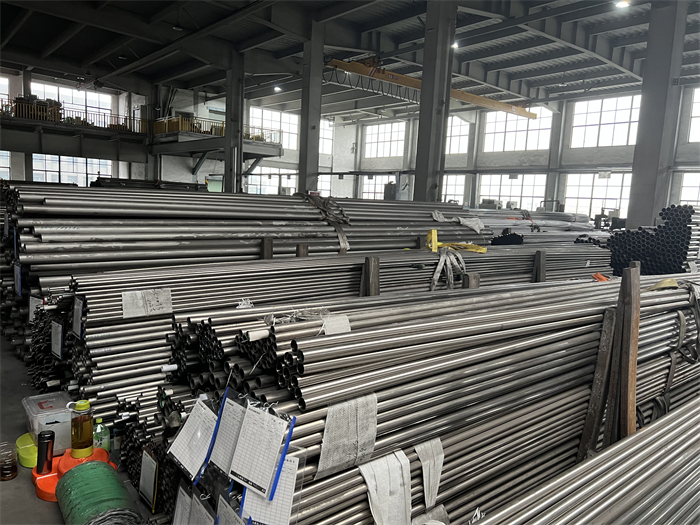
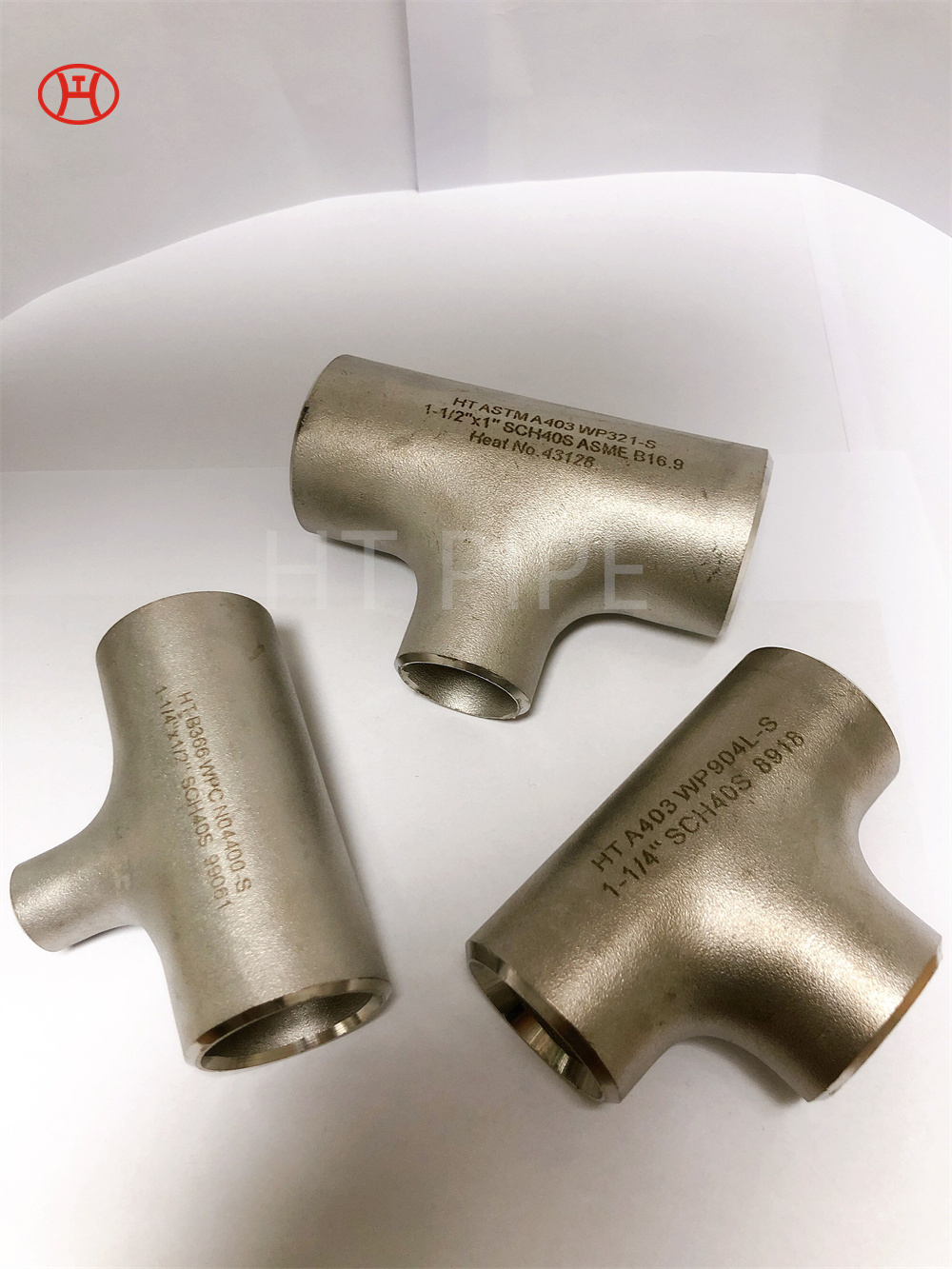
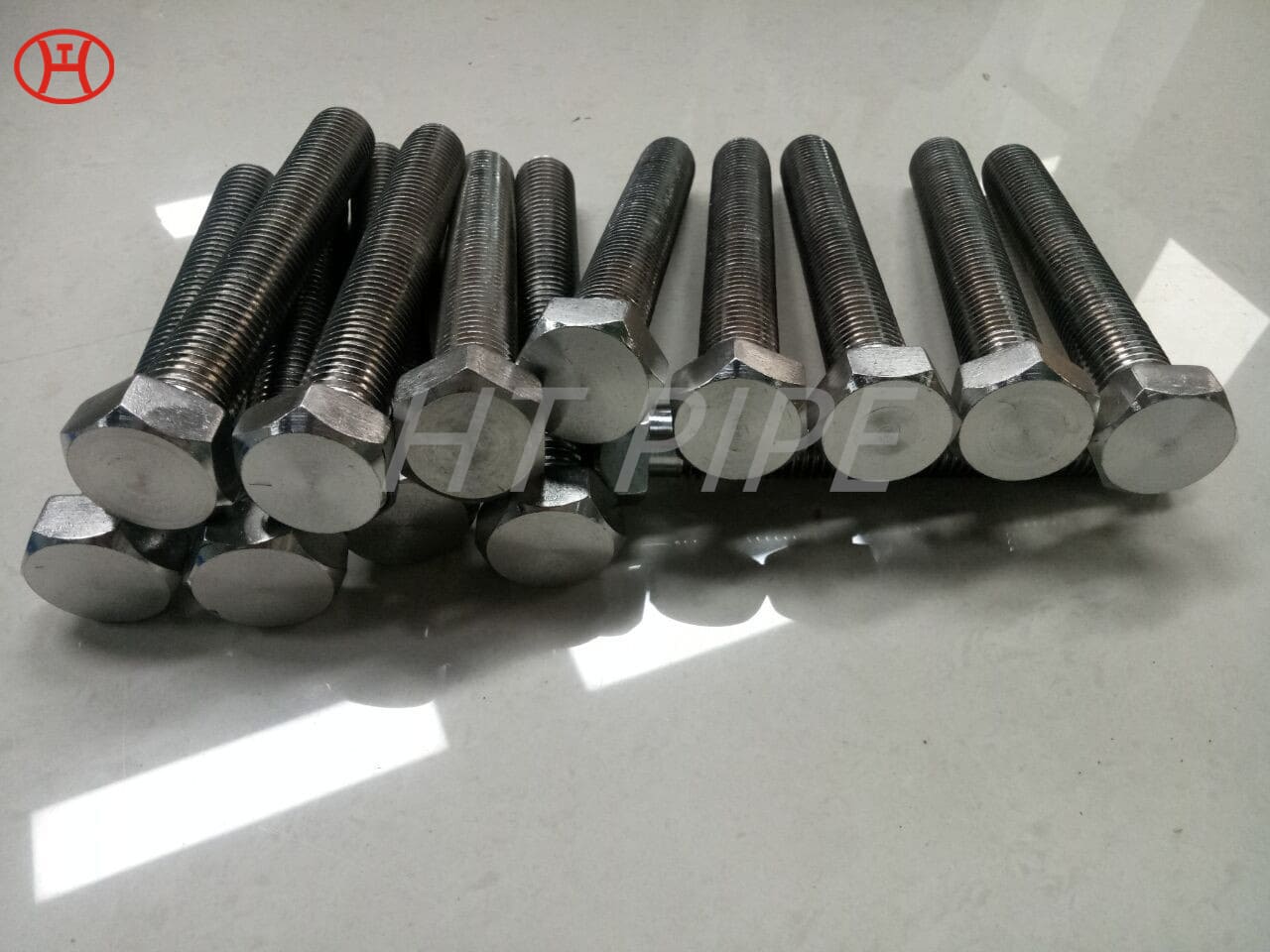
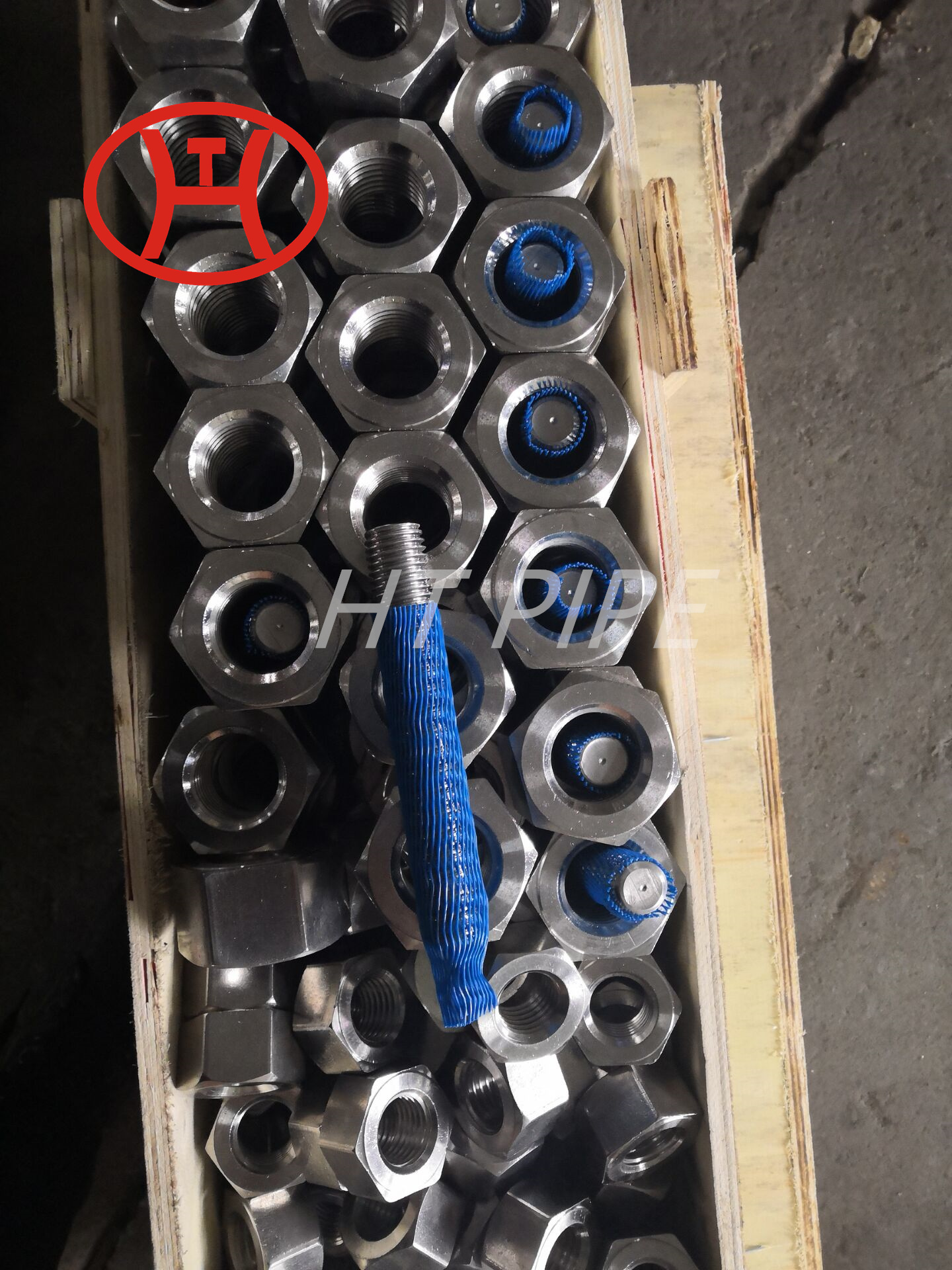
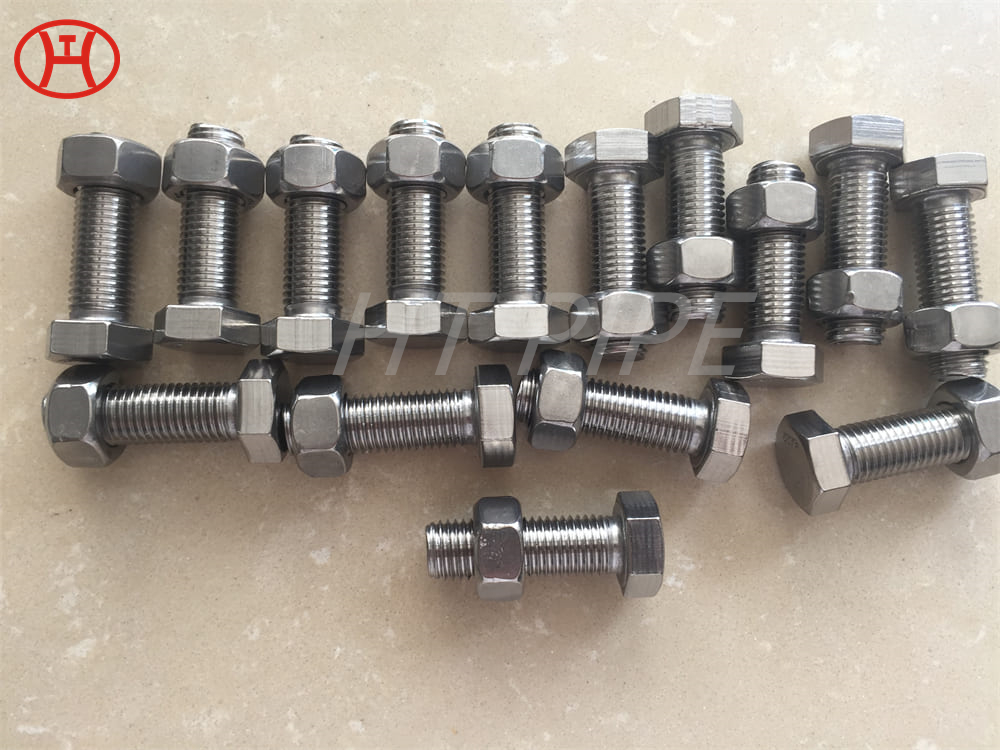
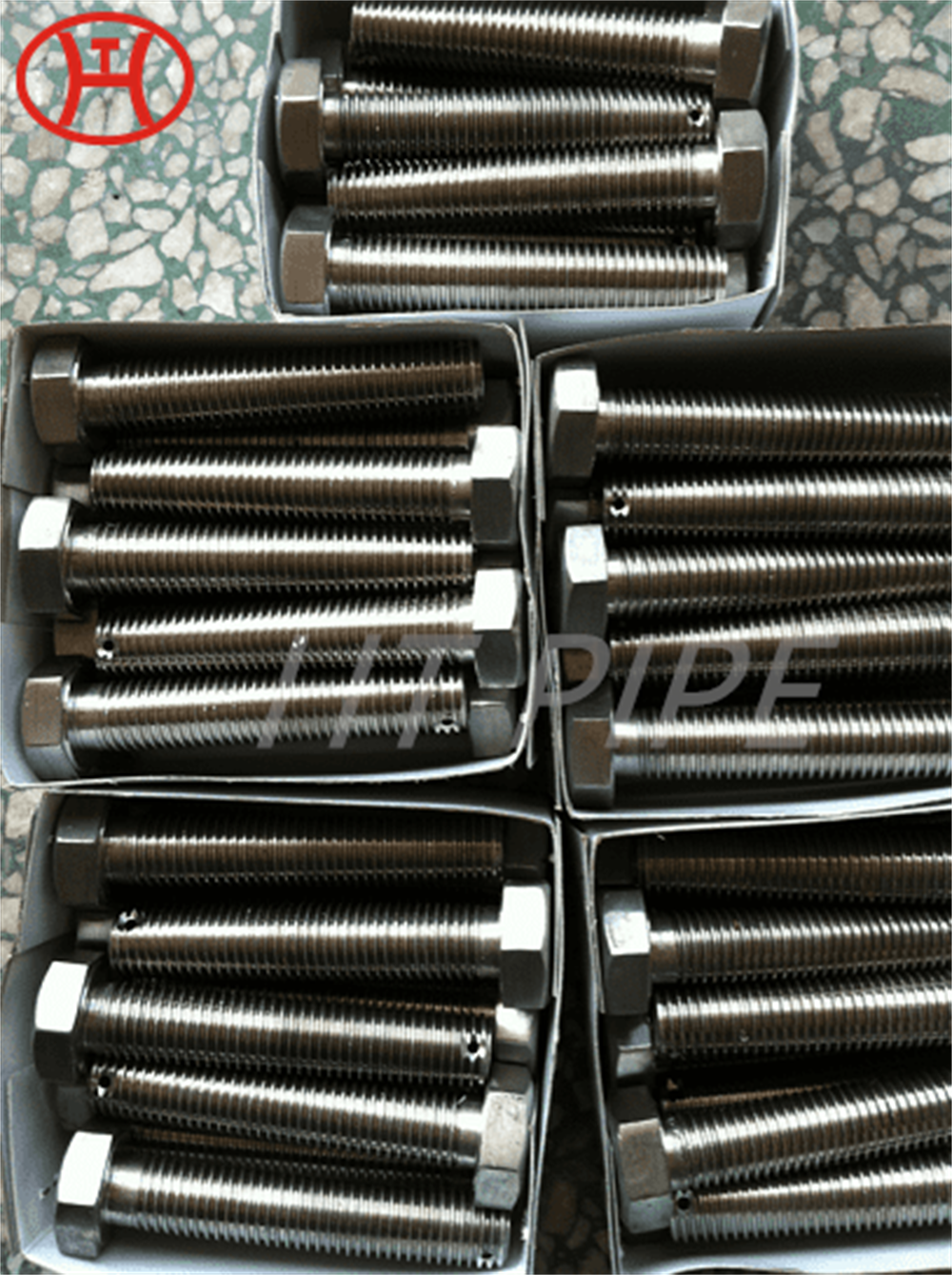
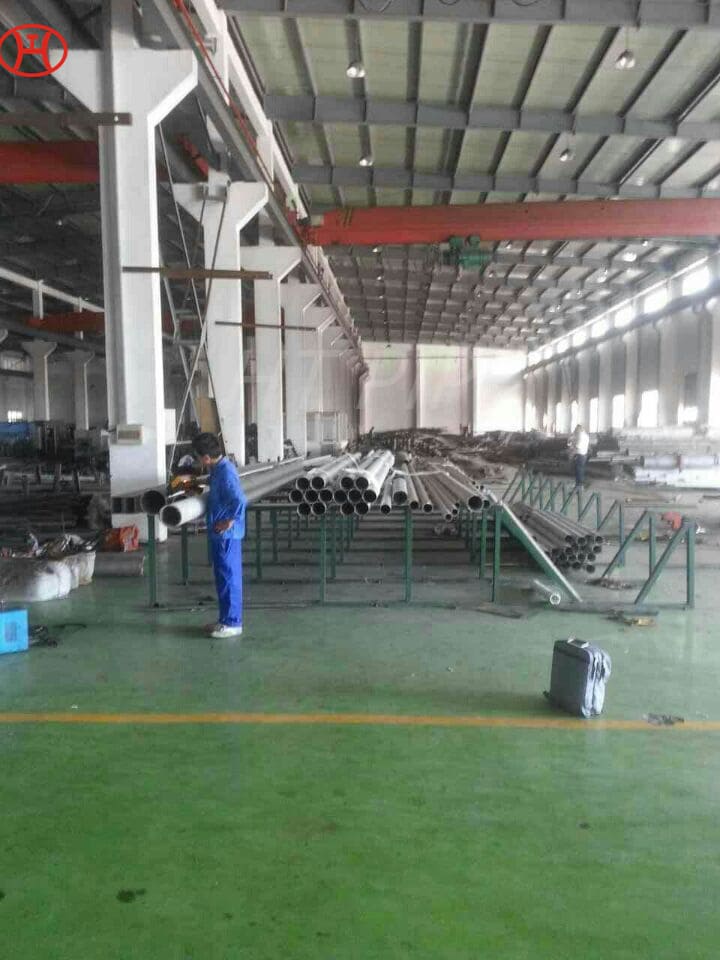
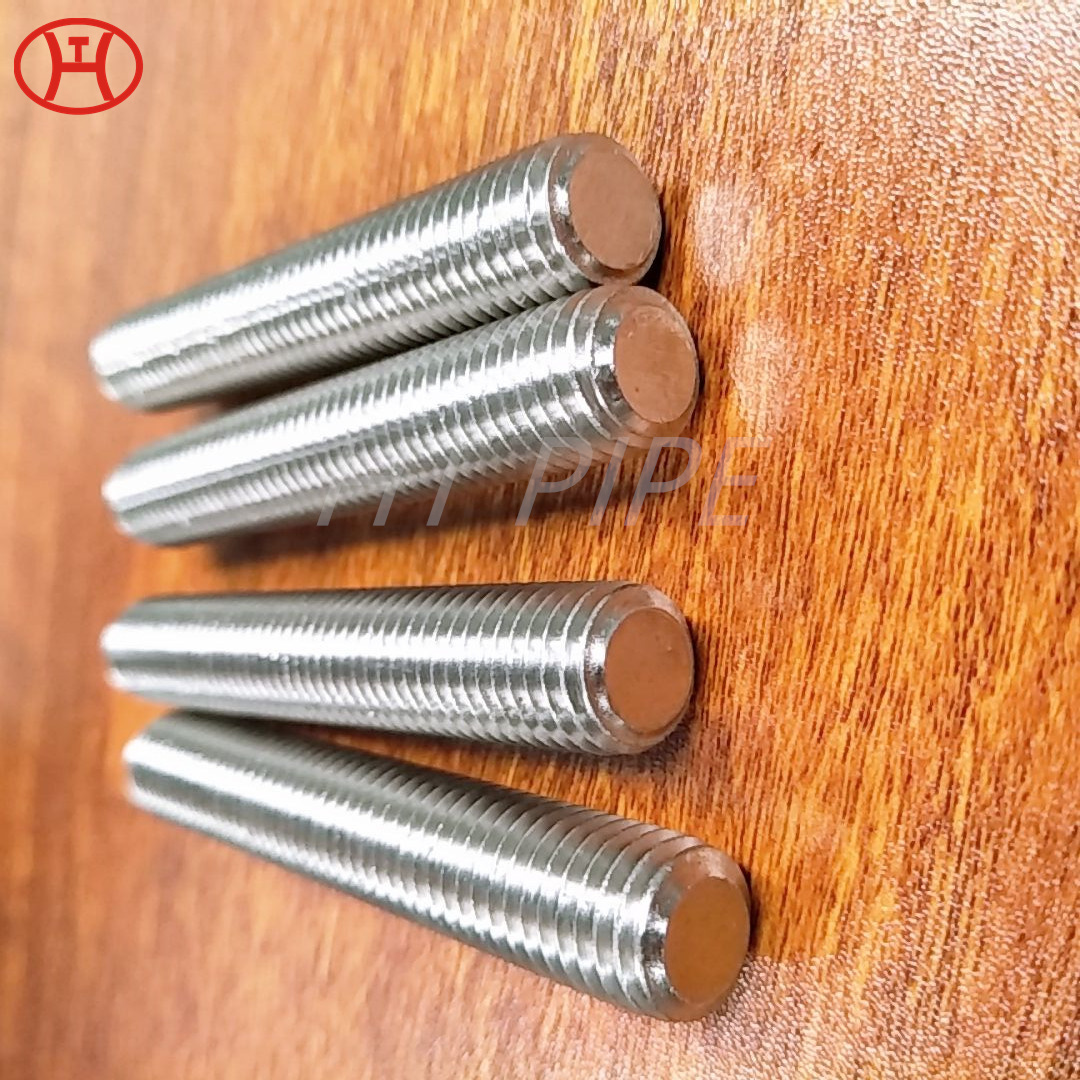
Stainless Steel 309 structural hex bolt 120-105 ksi minimum tensile strength
Stainless steel fasteners are used for corrosion resistance. Contrary to popular belief, stainless steel fasteners are not strong, but they do provide excellent resistance to rust, stains and corrosion. Stainless steel nuts, bolts, screws and washers should be your first choice when looking for fasteners that will fight the elements of the outdoors, especially water. The finish of stainless steel depends on the amount of chromium in the material.
Chromium-nickel stainless fastener, Alloy 309/309S Fastener, 309 Stainless Steel Bolt, UNS S30900 Nut
Alloy 309/309S is an austenitic heat resisting stainless steel. 23% chromium, approx. 5% more than 304 stainless steel gives Alloy 309/309S an edge over 304 stainless steel when it comes to general corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. Stainless steel is a popular material thanks to its durability and corrosion resistance. However, not all stainless steels are created equal—each type has different properties and uses. Today, we’re going to take a look at one of the most versatile types of stainless steel: 309 grade. Read on to learn more about the properties of this innovative alloy and some common applications for it.
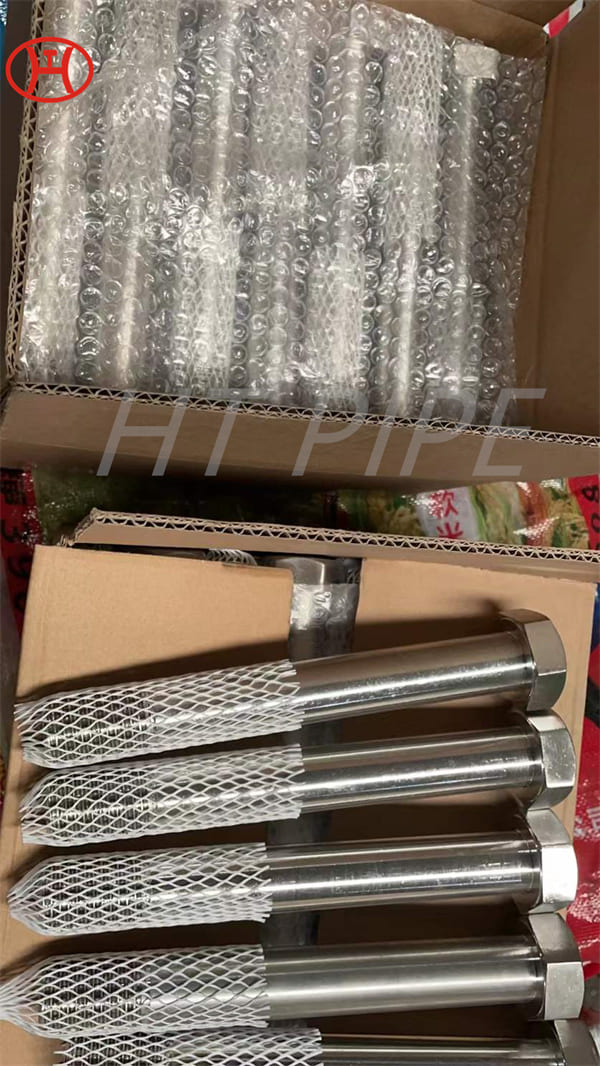

309 stainless steel bolt is versatile for a variety of industrial applications. This iron-nickel austenitic Bolt features impressive resistance to oxidation, carburization, and sulfur attack. The composition table of UNS S30900 Nut consists of percentages of chromium (24-26%), nickel (19-22%), and carbon (.25%). Other elements, such as silicon, manganese, nitrogen, and copper can also be found in small quantities. With its wide range of benefits, 309 is an essential component in the production of sheets and parts.
| Property | 309 |
| Density, lb/in3 | 0.285 |
| Modulus of Elasticity, psi | 29.0 x 106 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, 68-212˚F, /˚F | 8.7 x 10-6 |
| Thermal Conductivity, Btu/ft hr ˚F | 9.0 |
| Specific Heat, Btu/lb ˚F | 0.12 |
| Electrical Resistivity, Microohm-in | 30.7 |